Scientists Feared the World’s Smallest Snake Had Gone Extinct. They Just Found It Again
When fully grown, the Barbados threadsnake is only three to four inches long—shorter than many earthworms
This Surprising Ancient Reptile Had a Colorful, Corrugated Sail on Its Back. New Research Suggests It Was Used to Communicate
A 247-million-year-old fossil from a German natural history museum reveals the secrets of Mirasaura
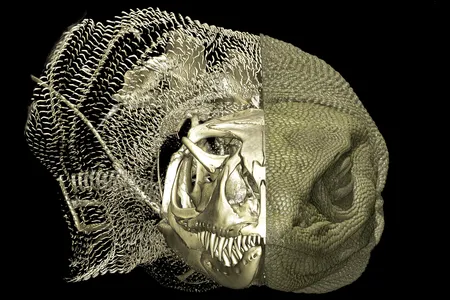
These Odd Bony Structures Were Hiding Beneath the Skin of Far More Lizards Than Thought, Researchers Find
Called osteoderms, the chain mail-like plates may have helped some species adapt to Australia’s harsh environment
‘Robo-Bunnies’ Are the Newest Weapon in the Fight Against Invasive Burmese Pythons in Florida
Scientists are experimenting with robotic rabbits in hopes of luring the destructive snakes out of hiding so they can be euthanized
Researchers Discover the Trick That Allows Burmese Pythons to Digest the Bones of Their Prey
Special intestinal cells collect excess minerals into particles the snakes can poop out, according to a new study
Smithsonian Photo Contest Galleries
See 15 Photos of Sensational, Slithering Snakes
These reptiles often get a bad rap, but there are plenty of reasons to celebrate snakes
A Paleontologist Matched Two Halves of the Same Fossil Stored at Different Museums—and Discovered a New Species
Meet Sphenodraco scandentis, a tree-dwelling, lizard-like reptile that roamed around with the dinosaurs during the Late Jurassic period roughly 145 million years ago
A Rare, Pregnant Ichthyosaur Fossil Discovered in Chile Is Revealing More Secrets About the Early Cretaceous World
The fossil helps scientists better understand not just the animal, but our planet’s geology
A Closer Look at the Kestrels, Hedgehogs and Other Wild Animals That Inhabit Rome
From antiquity to modern times, the city has been rife with creatures that creep, slither, scurry and nest among its pillars and palaces
These Lizards Mysteriously Survived the Asteroid Strike That Killed the Dinosaurs—and Their Descendants Are Still Alive Today
Small and elusive night lizards probably persisted because they have slow metabolisms and like to hide out in rock crevices, a new study suggests
After Crocs and Lemurs Went Extinct on the Mainland, Many Survived on Islands for Millions of Years
Isolation allows creatures to thrive as their relatives perish due to the threats present on much larger landmasses
A Jar of Fossil Bones Long Stored at a Museum Led Scientists to Discover a Goblin-Like Lizard From 76 Million Years Ago
Fossils described in a new study speak to a previously unknown large-bodied lizard diversity that existed alongside dinosaurs
A Large, Invasive Lizard Was Spotted in a California Park
Hikers at Joseph D. Grant County Park, just outside of San Jose, saw an Argentine black and white tegu last week—and rangers are now searching for the out-of-place reptile
Florida Bobcat Kills 13-Foot Python for the First Time on Record. It’s a Sign of Nature ‘Fighting Back’ Against the Invasive Snakes
Burmese pythons are wreaking havoc on the Everglades ecosystem, but some native animals have been known to prey on the enormous reptiles
Fossil Hunters Discover Earliest Known Footprints of a Reptile-Like Creature, Pushing Back the Timeline of Their Evolution
A new study suggests two fossil trackways found in Australia were made by an early amniote, a group that today includes reptiles, birds and mammals
This Eye-Catching Rattlesnake Found in Arizona Has Unusual ‘Leopard Spots,’ Likely From a Genetic Mutation
Snake wranglers safely relocated the healthy, female western diamondback from a backyard in Scottsdale, but they say the find is a first in their experience
The Famous, Feathered Dinosaur Archaeopteryx Could Fly, Suggests New Study of a ‘Beautifully Preserved’ Fossil
The Chicago Archaeopteryx features more soft tissue and delicate skeletal details than any known fossil of its kind, and paleontologists discovered it has a set of feathers key to flight in modern birds
200 Snakebites Later, One Man’s Blood May Hold the Key to a Universal Antivenom
Over two decades, Tim Friede has injected himself with snake venom hundreds of times, and subjected himself to more than 200 bites. Now, scientists are working on an antivenom derived from his antibodies
Fossils Reveal Enormous, Crocodile-Like Reptiles Survived for Millions of Years Longer Than Previously Thought
New discoveries in the Dominican Republic suggest sebecids roamed the Caribbean as recently as 4.5 million years ago, long after they vanished from South America
50-Million-Year-Old Footprints Open a ‘Rare Window’ Into the Behaviors of Extinct Animals That Once Roamed in Oregon
Scientists revisited tracks made by a shorebird, a lizard, a cat-like predator and some sort of large herbivore at what is now John Day Fossil Beds National Monument
Page 1 of 14