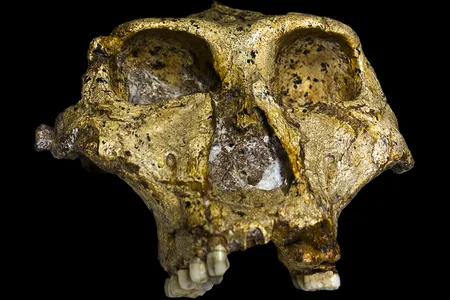
A Child’s Skull That Has Long Confounded Archaeologists Might Be a Human-Neanderthal Hybrid, Study Suggests
According to new CT scans and models, parts of the 140,000-year-old skull resemble those of modern humans, while the jaw appears to be more similar to those of our extinct relatives
See the Face of a 10,500-Year-Old Woman, Reconstructed by Archaeologists and Artists
Using well-preserved ancient DNA, researchers have created a life-like facial reconstruction of a woman who lived in Belgium’s Meuse Valley during the Mesolithic period
Iconic ‘Dragon Man’ Skull Offers First Glimpse of What a Denisovan’s Face Looked Like, New Genetic Studies Suggest
The mysterious ancient humans were only known from fossil fragments. Now, two papers argue a skull uncovered in China belongs to this group, after examining preserved DNA and proteins
Did a Neanderthal Who Lived 43,000 Years Ago Paint a Red Nose on a Rock That Looked Like a Face?
Researchers theorize that an adult male dipped his finger in red ocher and intentionally used the pigment to complete the face he saw on a small granite stone
Scientists Investigate 2.2-Million-Year-Old Tooth Enamel to Unravel the Mysteries of Ancient Human Relatives
By studying proteins preserved in teeth, researchers determined the sex of four Paranthropus robustus individuals that lived in southern Africa
Scientists Discover the Oldest Known Tools Made From Whale Bones, Crafted in Western Europe 20,000 Years Ago
Stone Age humans scavenged the skeletons of several whale species along the Bay of Biscay in what is now southwestern France and northern Spain, according to a new study
Scientists Use DNA to Trace Early Humans’ Footsteps From Asia to South America
Over thousands of years, humans from Eurasia trekked more than 12,400 miles to eventually reach the southernmost tip of South America, a new genetic investigation suggests
A Century Ago, a High School Teacher From a Small Tennessee Town Ignited a National Debate Over Human Evolution
The Scopes “monkey trial” garnered international attention, and the battle that was fought continues in some form in other states today
Nimble-Minded Neanderthals May Have Used These Wooden Spears to Hunt 200,000 Years Ago
New research shows that the weapons found in Germany are much younger than previously thought, suggesting they were made by skilled Neanderthal craftspeople
Human Evolution Traded Fur for Sweat Glands—and Now, Our Wounds Take Longer to Heal Than Those of Other Mammals
Even compared to chimpanzees, one of our closest relatives, humans’ scrapes and cuts tend to stick around for more than twice as long, new research suggests
Female Bonobos Assert Their Dominance Over Males by Banding Together, New Study Suggests
Bonobos, which are among our closest living relatives, live in rare societies where females tend to outrank males, even though males are larger and stronger. Scientists compiled decades of observations to explain why
Watch Wild Chimpanzees Share Alcoholic Fruit, a Behavior Just Captured on Video for the First Time
Though the reason behind this action is unclear, researchers suggest socially consuming alcohol may have offered evolutionary benefits to a common ancestor of both humans and chimps
Sunscreen, Clothing and Caves May Have Given Modern Humans an Edge Over Neanderthals When Earth’s Magnetic Field Wandered
A new study suggests the extinction of Neanderthals nearly coincided with a shift in Earth’s magnetic field that let more radiation reach the ground. Our species might have adapted more easily
Are These Mysterious 400,000-Year-Old Artifacts the Oldest Ivory Objects Made by Humans?
Found in Ukraine, the fragments show signs of human manipulation—though researchers still haven’t ruled out the possibility that they were shaped by natural forces
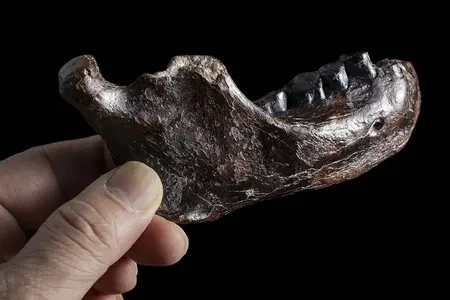
Mysterious Jawbone Found at an Antique Shop in Taiwan Belonged to a Male Denisovan, Scientists Say
The fossil, called Penghu 1, is one of the few known pieces of physical evidence from the Denisovans, extinct relatives of modern humans. It suggests the species lived in diverse environments
7,000-Year-Old Skeletons From the ‘Green Sahara’ Reveal a Mysterious Human Lineage
Researchers recently sequenced the genomes of two naturally mummified women found in Libya
There Might Be Something Human in the Way Bonobos Communicate—Their Calls Share a Key Trait With Our Language, Study Suggests
Researchers attempted to decode bonobo calls by recording their social context, then analyzed how the primates string together these vocalizations
Stone Tools Discovered in China Resemble Neanderthal Technology Used in Europe, Creating a Middle Stone Age Mystery
Archaeologists previously assumed that East Asia did not see considerable tool development during the Middle Paleolithic, but new findings might change that widely held idea
Researchers Unearth Oldest Known Human Facial Bones Ever Found in Western Europe
The upper jawbone and partial cheek bone represent a mysterious unknown species that lived in present-day Spain between 1.1 million and 1.4 million years ago, according to a new study
Mysterious Skeleton of Child With Human and Neanderthal Traits Has Finally Been Dated by Archaeologists
Discovered in Portugal in 1998, the individual dubbed the “Lapedo Child” has long perplexed scientists, thanks to a curious mix of features
Page 1 of 21