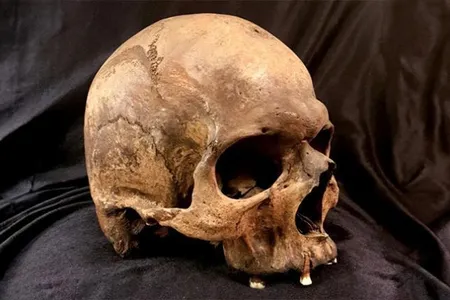
With Ancient DNA, Scientists Have Mapped 37,000 Years of Disease Across Europe and Asia
Zoonoses—diseases that spread from animals to humans—began to gain prevalence some 6,500 years ago with the rise of animal husbandry, a new study suggests
Scientists Recover Ancient Proteins From Animal Teeth Up to 24 Million Years Old, Opening Doors to Learning About the Past
Two new papers analyze fossils found in Canada and Kenya, respectively—vastly different environments for the preservation of genetic material
Greenland Sled Dog DNA Reveals a Story of Human Migration and Ancestry of the Unique Breed
Researchers analyzed ancient and modern genetic samples of the Greenlandic Qimmit breed to shed light on the long relationship between the Inuit and their dogs in the Arctic
These ‘Weird’ Sea Spiders Don’t Have Abdomens—and Instead Store Organs in Their Legs. With DNA, Scientists Are Learning Why
Researchers sequenced the knotty sea spider’s genome for the first time, revealing a missing gene that many other animals have
Something Strange Is Happening to Tomatoes Growing on the Galápagos Islands
Scientists say wild tomato plants on the archipelago’s western islands are experiencing “reverse evolution” and reverting back to ancestral traits
Scientists Have Sequenced an Ancient Egyptian Skeleton’s Entire Genome for the Very First Time. Here’s What They Found
Dating back more than 4,500 years, the skeleton belonged to a middle-aged man who may have worked as a potter and likely descended from ancestors in North Africa and Mesopotamia
These Cod Have Been Shrinking Dramatically for Decades. Now, Scientists Say They’ve Solved the Mystery
Eastern Baltic cod grow to much smaller sizes than they did just 30 years ago, because overfishing altered their genes, according to new research
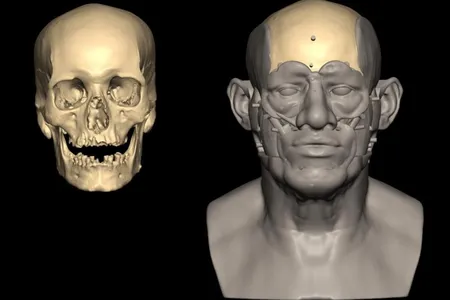
See the Face of a 10,500-Year-Old Woman, Reconstructed by Archaeologists and Artists
Using well-preserved ancient DNA, researchers have created a life-like facial reconstruction of a woman who lived in Belgium’s Meuse Valley during the Mesolithic period
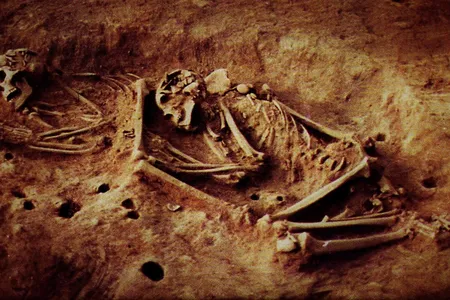
Ancient DNA Reveals Mysterious New Group of Humans in Colombia With No Genetic Ties to People Today
The previously undocumented lineage of hunter-gatherers seems to have disappeared around 2,000 years ago
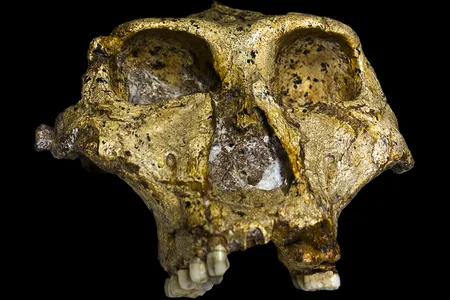
Scientists Investigate 2.2-Million-Year-Old Tooth Enamel to Unravel the Mysteries of Ancient Human Relatives
By studying proteins preserved in teeth, researchers determined the sex of four Paranthropus robustus individuals that lived in southern Africa
South Korea’s Female Free Divers May Have Evolved to Thrive Underwater, Study Finds
The Haenyeo, a group of skilled divers on Jeju Island, plunge beneath the ocean’s surface without any breathing equipment, thanks to a combination of their training and genetics
Scientists Use DNA to Trace Early Humans’ Footsteps From Asia to South America
Over thousands of years, humans from Eurasia trekked more than 12,400 miles to eventually reach the southernmost tip of South America, a new genetic investigation suggests
In a Remarkable First, a Baby With a Rare Disease Receives Personalized Gene Therapy
Researchers say the CRISPR-based technique used could eventually be employed to treat more people with rare genetic diseases
This Eye-Catching Rattlesnake Found in Arizona Has Unusual ‘Leopard Spots,’ Likely From a Genetic Mutation
Snake wranglers safely relocated the healthy, female western diamondback from a backyard in Scottsdale, but they say the find is a first in their experience
‘1 Out of Every 100,000’: This Rare Piebald Elk Is Turning Heads in Colorado With Her Unusually Splotchy Fur
The female ungulate has white patches on her face and body, likely because of an uncommon genetic condition that affects pigmentation
DNA Links Modern Picuris Pueblo Tribe to Ancestors Who Lived in Chaco Canyon Hundreds of Years Ago
Tribal leaders partnered with scientists to confirm their connection to the archaeological site in New Mexico
Scientists in Australia Mapped the Genome of an Endangered Frog Species in an Effort to Save It
A deadly fungus threatens the southern corroboree frog, which needs a lot of help to survive
Carthaginians, Ancient Rome’s Infamous Enemies, Are Not Exactly Who Scholars Thought They Were, Ancestry Study Suggests
DNA reveals that the people of Carthage, a powerful independent colony founded by the Phoenicians, had little genetic similarity to their counterparts in the Levant
Why Do Mosquitos Bite Some People More Than Others? Your Blood Type, Sweat Contents and Even Alcohol Consumption May Make You More Attractive to the Pesky Insects
Scientists are working hard to discover the factors that drive the blood-sucking insects to target certain individuals
The Ancient ‘Terror Crocodiles’ of North America Weren’t Alligators After All, DNA and Fossils Suggest
A new study indicates the giant reptile Deinosuchus is not a close relative of modern alligators, as scientists previously thought, and it might have thrived by tolerating saltwater
Page 1 of 34